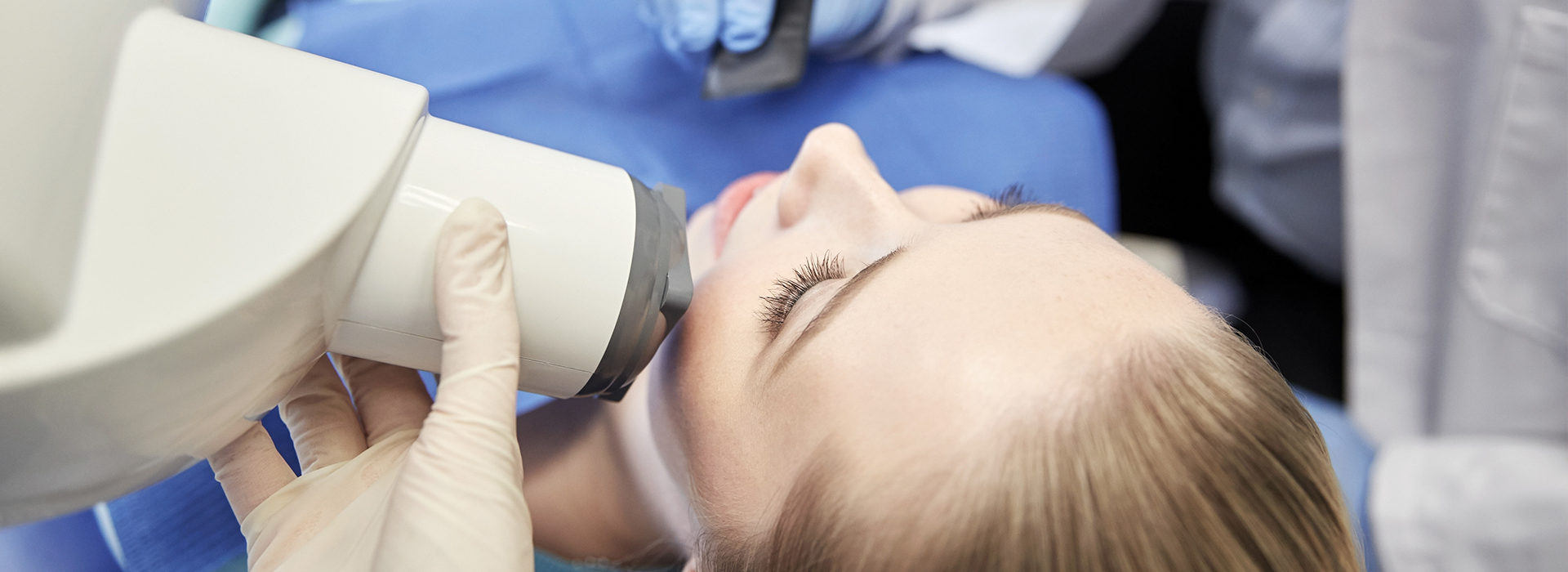
Digital radiography utilizes computer technology and digital sensors for the acquisition, viewing, storage, and sharing of radiographic images. It offers several advantages over the older traditional film based methods of taking x-rays. The most significant of these advantages is that digital radiography reduces a patient’s exposure to radiation. Other benefits are that images can be viewed instantly after being taken, can be seen simultaneously as needed by multiple practitioners, and can be easily shared with other offices. Digital x-rays are also safer for the environment as they do not require any chemicals or paper to develop.
An electronic pad, known as a sensor is used instead of film to acquire a digital image. After the image is taken, it goes directly into the patient’s file on the computer. Once it is stored on the computer, it can be easily viewed on a screen, shared, or printed out.
In dentistry the most common indications for cone-beam imaging are assessment of the jaws for placement of dental implants, evaluation of the temporomandibular joints for osseous degenerative changes, examination of teeth and facial structures for orthodontic treatment planning, evaluation of the proximity of lower wisdom teeth to the mandibular nerve prior to extraction, and evaluation of teeth and bone for signs of infections, cysts, or tumors.
